Special Cutouts Guide - V11

Watch our Special Cutouts Video on our YouTube Channel.
Special Cutouts
The Special Cutouts page of the Cabinet Machining
category makes it possible to add one special cutout to each cabinet component.
When
you first look at this screen it can feel a little bewildering. However, once
familiar with it, it is not as bad as it looks. We will first discuss the rules
and then the options associated with each selection and examples of cutouts.
Rules
- Up to three separate cutouts can be applied to
each cabinet. These can be Circles (including semicircles and quarter circles),
Rectangles or Slots.
- For Circles and Rectangles you specify the dimensions and the position of the centre.
- For Slots you specify (1) the Width, (2) which edge it is cut from and (3) the location of its end.
- Slots are always cut with a semicircular end, beyond the selected end point.
- Depending on their position, Circles are reduced to arcs if the circle would otherwise be part of the component. If the centre is within the radius of an edge, the centre automatically moves itself to be on the edge. Thus only full circles, semicircles or quarter circles are actually cut.
- A similar approach is taken for Rectangles, as for Circles, regarding their size (using the Width or Height instead of the Radius). For rectangles, the radius is applied to the corners.
- The centre of a Rectangle, Circle, or the end point of a Slot is specified either as exact co-ordinates or relative positions on the component, from a chosen starting corner. For example, a centre may be positioned 100mm across a component from its bottom left and half way up, by selecting ‘BotL’ as the start position, ‘0’ as the ‘x Fraction’, ‘100mm’ as the ‘x Pos’ and ‘0.5’ as the ‘y Fraction’.
- Holes for centres placed off the component will be positioned as if centred on the edge of the component.
- If a specified width, height or radius exceeds the width or height of the component, it will be ignored.
- These cutouts are undertaken without any regard to any other machining options (for example, screw holes drilled to fix the component to another). The user is therefore responsible for the effect this may have.
- Cutouts applied to Shelves will be applied to ALL shelves in the cabinet.
Options
Use | Whether or not the cutout is
in use |
Part | To which part (component) the cutout is to be applied. |
Type of Cutout | Choose None, Circle, Rectangle, or
Slot. |
Radius | Required by the Circle and rectangles corners. |
Width | Required by the Rectangle and Slot. |
Height | Required by the Rectangle only |
Side | Required by Slots only. Determines the side in which the slot is cut from. |
Start | The start
position from where to calculate the centre/end point. The options are
‘TopL’, ‘TopR’, ‘BotL’ or ‘BotR’.
These refer to the corners of the component as it is viewed from the
chosen machining face. See the ‘Face’ page of the Catalog/ Drawing properties. |
x Fraction | One way of specifying the position of the centre/slot end point. It represents a fraction of the component’s width, from the chosen start position. Values can be between 0 and 1. Example: Here the resulting position would be halfway across the component (regardless of the components size.) Regardless of the start position, the ‘x Fraction’ always positions away from the chosen start point, there is no need to try and use negative numbers. (e.g. 0.5 from TopR would result in the same position as from TopL). |
x Pos | The alternative method of specifying the position of the centre/slot end point. It represents an actual distance from the chosen start position. Example: Here the resulting position would be 100mm from the bottom left hand corner. Regardless of the start position, the ‘xPos’ always positions away from the chosen start point, there is no need to try and use negative numbers. (e.g. 100mm from Top Right would result in a position 100mm towards the Top Left). xPos can be combined with x Fraction. Example: To centre circle 30mm from the centre use ‘0.5’ as x Fraction and ‘30mm’ as xPos, from the appropriate starting corner. |
y Fraction | Similar to x Fraction but dealing with the position of the centre/slot end point in relation to the component's height. |
y Pos | Similar to xPos but dealing with the position of the centre/slot end point in relation to the component’s height. |
Examples of Special Cutouts
To view cutouts for Machining in the Preview
Pane, select options on the View page of the Cabinet Machining category. i.e.
turn on the View checkbox and select part to view from the dropdown.
1 - Circle
Use options Radius, Start, x Pos, y Pos:
This would cut a circle of radius
50mm in the Left End.
The
centre of the circle being 200mm to the left of and 400mm down from the top
right corner of the component.
2 - Semi Circle
Use
options
Radius, y Pos:
Similar to the example above, but
this would cut a semicircle of
radius 50mm in the Left End.
The centre being 200mm to the
left of the top right corner and on the edge of the component.
This
is because the yPos is less than the radius, so the circle would have been cut
off. As mentioned in the ‘Rules’ above, when this happens the centre is placed on the edge of the component.
3 - Slot
Use options Type, Width, Side:
: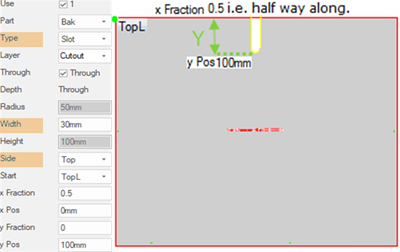
Cuts a slot in the Back component, of width
30mm, down from the Top of the component to a position 100mm below the top and halfway
along.
4 - Rectangle 1
Use options Type, Radius, x / y Fractions, yPos:
Cuts out a rectangle into the Bottom part
component, 75mm wide and 100m high, centred 20mm above the middle of the
component. The corners being cut with 20mm radius.
5 - Rectangle 2
Use options Type, Radius, Start:
As the centre of the rectangle is the bottom
left hand corner, this results in a cutout from the part of only 37.5mm wide
and 50mm high. The corners being cut with 20mm radius.

TIP: Click the attachment to download this HowTo to your desktop as a .pdf
Related Articles
Special cutouts guide
Special Cutouts The Special Cutouts page of the Cabinet Machining category makes it possible to add one special cutout to each cabinet component. When you first look at this screen it can feel a little bewildering. However, once familiar with it, it ...Customising a cabinet in CabMaster Software
Customise a Cabinet Cabinets can be customised before or after they are placed on the drawing. For comprehensive discussions see also the following: CabMasterPro Help topics [F1] : Topic Discusses Cabinet Properties Different ways to select cabinets ...Panel Estimator Help Guide
For detailed information on Panel Estimator, please follow this link HERE. You can also find the help document for Panel Estimator attached to this article.Shelf Heights and Cutouts - V11
Shelf Heights and Cutouts V11 This document will discuss shelf heights for: 1. Typical shelves which are automatically spaced inside a carcass 2. Shelves in Tall Standard which allow for comprehensive shelf adjustments o ...CabMaster RDL Reporting Getting Started Guide
Please note that editing and designing your own report is not part of support, if you would like a customized report then that can be arranged for if you contact your local Sales Representative. Getting Started Required Software Microsoft Report ...